 |
|
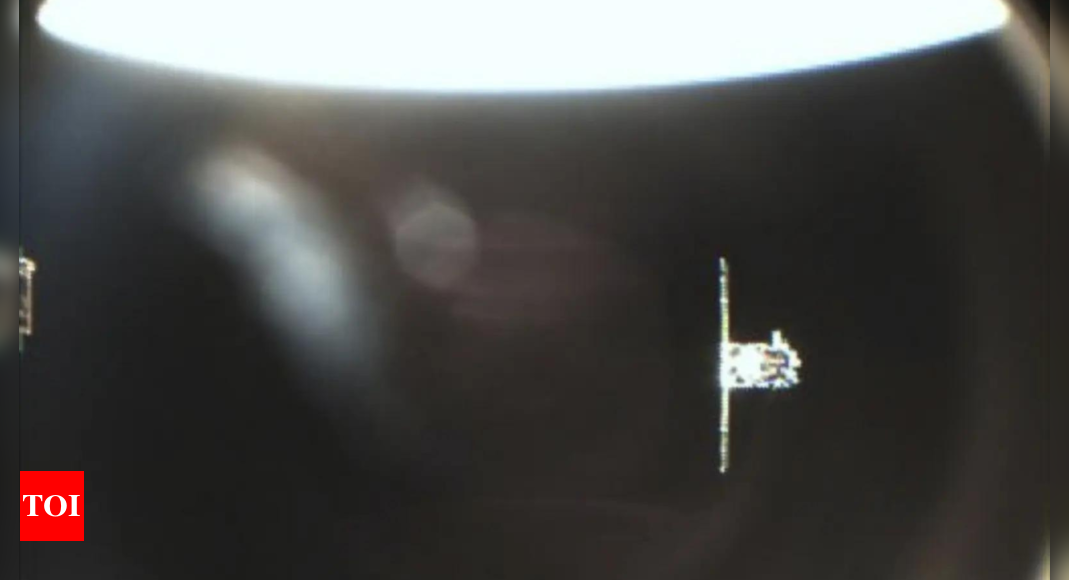
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) recently conducted the Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX), a crucial step towards enabling future human spaceflight missions, particularly the ambitious Gaganyaan project. The selection of the mission's orbital parameters – a 475km altitude and a carefully chosen inclination – was not arbitrary. ISRO meticulously planned the experiment to ensure compatibility with the requirements of human spaceflight while simultaneously mitigating risks associated with potential abort scenarios. The 475km orbit, slightly higher than the typical human presence orbit (370-450km), provides an added margin of safety, minimizing the likelihood of the satellites falling into populated areas in case of an emergency. The inclination of the orbit, on the other hand, was chosen to ensure adequate coverage of global landmasses for observation and data collection, further optimizing the mission's scientific goals. This careful selection of parameters reflects ISRO's commitment to both scientific achievement and the safety of its astronauts.
A critical element of the SpaDeX mission was the deployment of an extensive tracking network. ISRO leveraged not only its own network of 18 tracking stations but also incorporated the services of 24 additional commercial tracking stations worldwide. This comprehensive approach maximized the visibility of the satellites, allowing for continuous monitoring throughout the experiment. The utilization of multiple tracking stations across the globe underscores the complexity of the docking maneuver and the importance of precise tracking data for such a sensitive mission. This multifaceted tracking network served as a vital rehearsal for the Gaganyaan mission, providing valuable experience in coordinating and managing a global tracking infrastructure for future human spaceflights. The seamless integration of domestic and international tracking resources is a testament to ISRO's capabilities in international collaboration and its preparation for the challenges of human space exploration.
Beyond the logistical and safety considerations, the SpaDeX mission also incorporated significant scientific payloads. Each of the two satellites involved carried an imaging payload designed to demonstrate and refine high-performance capabilities in compact, nano-sized satellites. This technology demonstration is crucial for developing more efficient and cost-effective remote sensing satellites in the future. These smaller, more technologically advanced satellites represent a potential breakthrough in space technology, enabling more complex scientific missions with reduced cost and increased efficiency. Further enhancing the scientific scope, a radiation monitoring payload was also deployed to assess electron and proton radiation levels in the chosen orbit. This data is extremely valuable for future human spaceflights, as radiation exposure poses a significant health risk to astronauts. Understanding radiation levels and their fluctuations is paramount in developing effective shielding and countermeasures to protect the well-being of astronauts during longer-duration space missions. The information gathered during SpaDeX is directly applicable to Gaganyaan, informing crucial safety protocols and technological developments.
Following the successful docking of the two satellites, the mission team is currently analyzing the data gathered and evaluating the overall success of the operation. The decision to attempt further docking maneuvers will depend on the remaining fuel reserves and any identified requirements for further verification. The scientific payloads on board, including the imaging and radiation monitoring systems, will only be activated after the satellites have successfully separated. This phased approach prioritizes the successful completion of the critical docking and undocking procedures before progressing to the scientific data acquisition phase. The methodical approach to the mission highlights ISRO's dedication to rigorous testing and validation, essential for the success of future human spaceflight endeavors. The lessons learned from SpaDeX will undeniably contribute significantly to the preparation and execution of the ambitious Gaganyaan program, demonstrating ISRO’s preparedness for ambitious future objectives.
In conclusion, the ISRO's SpaDeX mission serves as a significant milestone in India's space exploration program. The successful completion of the docking maneuver, the utilization of a global tracking network, and the deployment of cutting-edge scientific payloads all contribute to the preparation for future human spaceflights. The mission's attention to detail, meticulous planning, and focus on safety underscore ISRO's commitment to achieving its ambitious goals while prioritizing the well-being of its astronauts. SpaDeX’s success underscores the advancements India is making in space technology and demonstrates its ability to contribute significantly to the global space exploration community. Further analysis of the gathered data will undoubtedly provide invaluable insights for future missions, accelerating India's progress in human space exploration.
Source: Orbit for docking satellites chosen keeping human missions in mind
